Introducing Hot Reloading
React Native's goal is to give you the best possible developer experience. A big part of it is the time it takes between you save a file and be able to see the changes. Our goal is to get this feedback loop to be under 1 second, even as your app grows.
We got close to this ideal via three main features:
- Use JavaScript as the language doesn't have a long compilation cycle time.
- Implement a tool called Packager that transforms es6/flow/jsx files into normal JavaScript that the VM can understand. It was designed as a server that keeps intermediate state in memory to enable fast incremental changes and uses multiple cores.
- Build a feature called Live Reload that reloads the app on save.
At this point, the bottleneck for developers is no longer the time it takes to reload the app but losing the state of your app. A common scenario is to work on a feature that is multiple screens away from the launch screen. Every time you reload, you've got to click on the same path again and again to get back to your feature, making the cycle multiple-seconds long.
Hot Reloading
The idea behind hot reloading is to keep the app running and to inject new versions of the files that you edited at runtime. This way, you don't lose any of your state which is especially useful if you are tweaking the UI.
A video is worth a thousand words. Check out the difference between Live Reload (current) and Hot Reload (new).
If you look closely, you can notice that it is possible to recover from a red box and you can also start importing modules that were not previously there without having to do a full reload.
Word of warning: because JavaScript is a very stateful language, hot reloading cannot be perfectly implemented. In practice, we found out that the current setup is working well for a large amount of usual use cases and a full reload is always available in case something gets messed up.
Hot reloading is available as of 0.22, you can enable it:
- Open the developer menu
- Tap on "Enable Hot Reloading"
Implementation in a nutshell
Now that we've seen why we want it and how to use it, the fun part begins: how it actually works.
Hot Reloading is built on top of a feature Hot Module Replacement, or HMR. It was first introduced by Webpack and we implemented it inside of React Native Packager. HMR makes the Packager watch for file changes and send HMR updates to a thin HMR runtime included on the app.
In a nutshell, the HMR update contains the new code of the JS modules that changed. When the runtime receives them, it replaces the old modules' code with the new one:
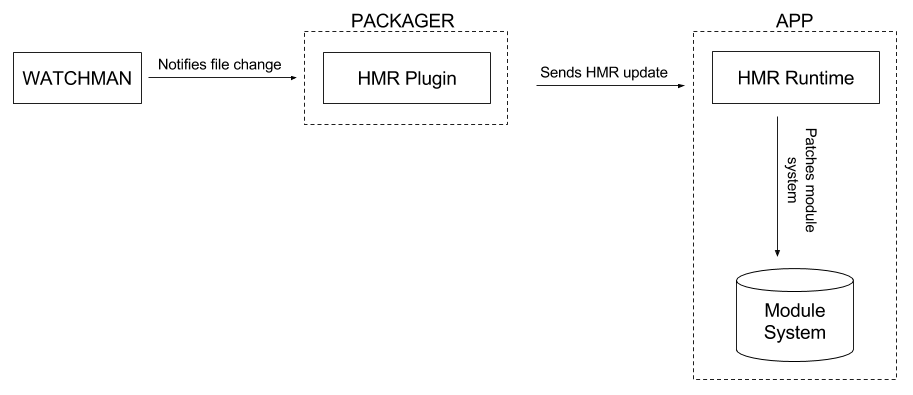
The HMR update contains a bit more than just the module's code we want to change because replacing it, it's not enough for the runtime to pick up the changes. The problem is that the module system may have already cached the exports of the module we want to update. For instance, say you have an app composed of these two modules:
// log.js
function log(message) {
const time = require('./time');
console.log(`[${time()}] ${message}`);
}
module.exports = log;
// time.js
function time() {
return new Date().getTime();
}
module.exports = time;
The module log, prints out the provided
message including the current date provided by the module
time.
When the app is bundled, React Native registers each
module on the module system using the
__d function. For this app, among many
__d definitions, there will one for
log:
__d('log', function() {
... // module's code
});
This invocation wraps each module's code into an anonymous function which we generally refer to as the factory function. The module system runtime keeps track of each module's factory function, whether it has already been executed, and the result of such execution (exports). When a module is required, the module system either provides the already cached exports or executes the module's factory function for the first time and saves the result.
So say you start your app and require log. At
this point, neither log nor
time's factory functions have been executed
so no exports have been cached. Then, the user modifies
time to return the date in
MM/DD:
// time.js
function bar() {
var date = new Date();
return `${date.getMonth() + 1}/${date.getDate()}`;
}
module.exports = bar;
The Packager will send time's new code to the runtime
(step 1), and when log gets eventually
required the exported function gets executed it will do so
with time's changes (step 2):
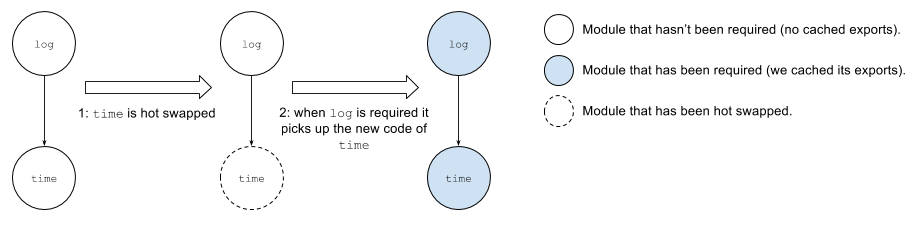
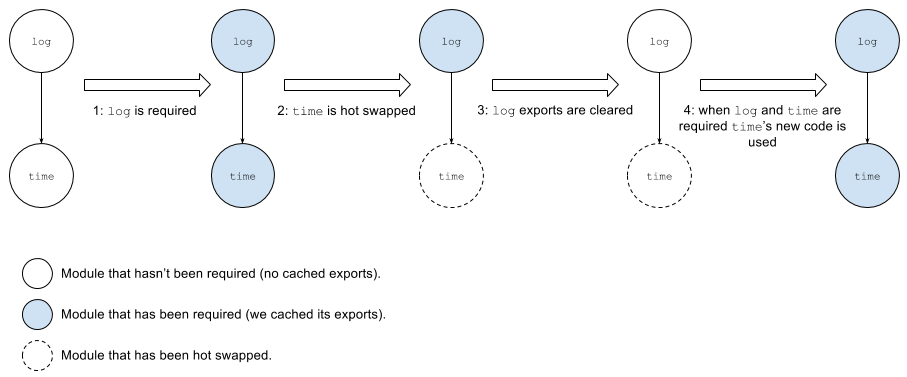
Now say the code of log requires
time as a top level require:
const time = require('./time'); // top level require
// log.js
function log(message) {
console.log(`[${time()}] ${message}`);
}
module.exports = log;
When log is required, the runtime will cache
its exports and time's one. (step 1). Then,
when time is modified, the HMR process cannot
simply finish after replacing time's code. If
it did, when log gets executed, it would do
so with a cached copy of time (old code).
For log to pick up time changes,
we'll need to clear its cached exports because one of the
modules it depends on was hot swapped (step 3). Finally,
when log gets required again, its factory
function will get executed requiring time and
getting its new code.
HMR API
HMR in React Native extends the module system by
introducing the hot object. This API is based
on
Webpack's one. The hot object exposes a function
called accept which allows you to define a
callback that will be executed when the module needs to be
hot swapped. For instance, if we would change
time's code as follows, every time we save
time, we'll see “time changed” in the console:
// time.js
function time() {
... // new code
}
module.hot.accept(() => {
console.log('time changed');
});
module.exports = time;
Note that only in rare cases you would need to use this API manually. Hot Reloading should work out of the box for the most common use cases.
HMR Runtime
As we've seen before, sometimes it's not enough only
accepting the HMR update because a module that uses the
one being hot swapped may have been already executed and
its imports cached. For instance, suppose the dependency
tree for the movies app example had a top-level
MovieRouter that depended on the
MovieSearch and
MovieScreen views, which depended on the
log and time modules from the
previous examples:
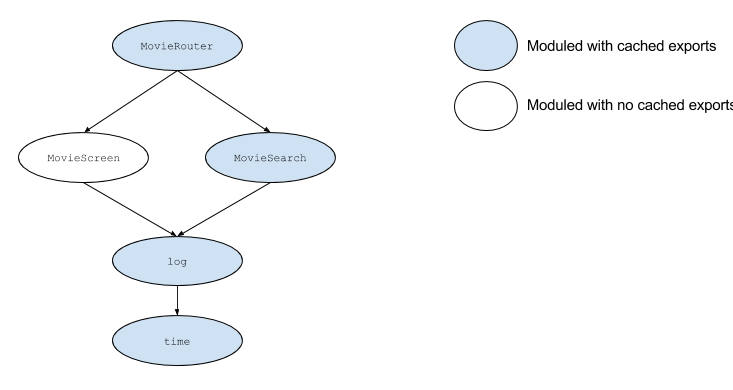
If the user accesses the movies' search view but not the
other one, all the modules except for
MovieScreen would have cached exports. If a
change is made to module time, the runtime
will have to clear the exports of log for it
to pick up time's changes. The process
wouldn't finish there: the runtime will repeat this
process recursively up until all the parents have been
accepted. So, it'll grab the modules that depend on
log and try to accept them. For
MovieScreen it can bail, as it hasn't been
required yet. For MovieSearch, it will have
to clear its exports and process its parents recursively.
Finally, it will do the same thing for
MovieRouter and finish there as no modules
depends on it.
In order to walk the dependency tree, the runtime receives the inverse dependency tree from the Packager on the HMR update. For this example the runtime will receive a JSON object like this one:
{
modules: [
{
name: 'time',
code: /* time's new code */
}
],
inverseDependencies: {
MovieRouter: [],
MovieScreen: ['MovieRouter'],
MovieSearch: ['MovieRouter'],
log: ['MovieScreen', 'MovieSearch'],
time: ['log'],
}
}
React Components
React components are a bit harder to get to work with Hot Reloading. The problem is that we can't simply replace the old code with the new one as we'd loose the component's state. For React web applications, Dan Abramov implemented a babel transform that uses Webpack's HMR API to solve this issue. In a nutshell, his solution works by creating a proxy for every single React component on transform time. The proxies hold the component's state and delegate the lifecycle methods to the actual components, which are the ones we hot reload:
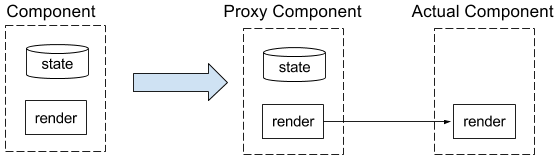
Besides creating the proxy component, the transform also
defines the accept function with a piece of
code to force React to re-render the component. This way,
we can hot reload rendering code without losing any of the
app's state.
The default
transformer
that comes with React Native uses the
babel-preset-react-native, which is
configured
to use react-transform the same way you'd use
it on a React web project that uses Webpack.
Redux Stores
To enable Hot Reloading on Redux stores you will just need to use the HMR API similarly to what you'd do on a web project that uses Webpack:
// configureStore.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import reducer from '../reducers';
export default function configureStore(initialState) {
const store = createStore(
reducer,
initialState,
applyMiddleware(thunk),
);
if (module.hot) {
module.hot.accept(() => {
const nextRootReducer = require('../reducers/index').default;
store.replaceReducer(nextRootReducer);
});
}
return store;
};
When you change a reducer, the code to accept that reducer
will be sent to the client. Then the client will realize
that the reducer doesn't know how to accept itself, so it
will look for all the modules that refer it and try to
accept them. Eventually, the flow will get to the single
store, the configureStore module, which will
accept the HMR update.
Conclusion
If you are interested in helping making hot reloading better, I encourage you to read Dan Abramov's post around the future of hot reloading and to contribute. For example, Johny Days is going to make it work with multiple connected clients. We're relying on you all to maintain and improve this feature.
With React Native, we have the opportunity to rethink the way we build apps in order to make it a great developer experience. Hot reloading is only one piece of the puzzle, what other crazy hacks can we do to make it better?
